Laser Cutting Machine Types: A Comprehensive
Technical Overview
1. Introduction
Laser cutting machines are advanced manufacturing tools that utilizehigh-powered laser beams to cut, engrave, or etch materials with high precision.They are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics,and metal fabrication due to their accuracy, speed, and versatility. Thisdocument provides a detailed classification of laser cutting machines based ontheir laser source, application, and operational mechanisms.
2. Classification of Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines can be categorized based on:
Laser Source
Machine Configuration
Material Compatibility
2.1 By Laser Source
(1) CO₂ Laser Cutting Machines
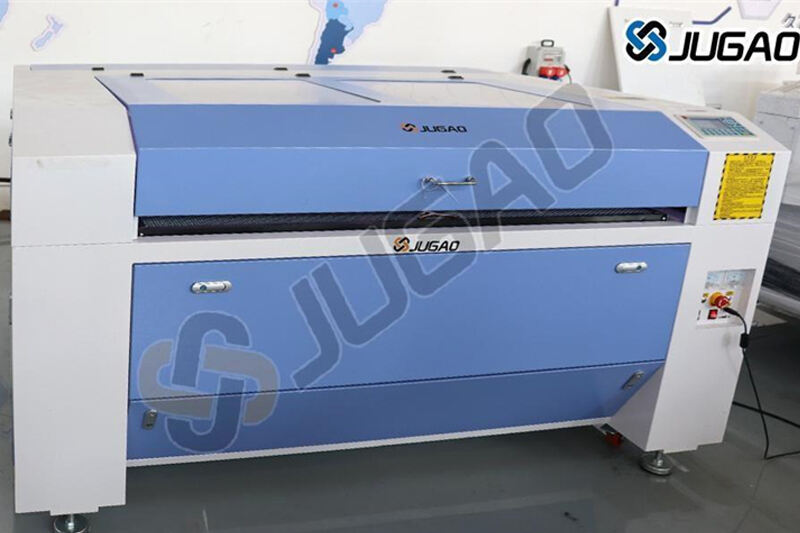

Working Principle: Uses a gas mixture (CO₂, nitrogen, and helium) excitedby electrical discharge to generate a laser beam (wavelength: 10.6 µm).
Applications:
Cutting non-metallic materials (wood, acrylic, leather, plastics).
Thin metal sheets (up to 20 mm, depending on power).
Advantages:
High efficiency for organic materials.
Smooth cutting edges.
Limitations:
Lower efficiency for highly reflective metals (copper, aluminum).
Higher maintenance due to gas refilling requirements.

(2) Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Working Principle: Uses a solid-state laser source where the beam isgenerated via doped optical fibers (wavelength: 1.06 µm).
Applications:
Ideal for metals (steel, aluminum, brass, copper).
High-speed precision cutting (up to 50 mm thickness).
Advantages:
Higher energy efficiency (~30% vs. CO₂’s ~10%).
Lower maintenance (no gas or mirrors required).
Better for reflective metals.
Limitations:
Less effective for non-metals.

(3) Nd:YAG/Nd:YVO₄ Laser Cutting Machines
Working Principle: Solid-state lasers using neodymium-doped crystals(wavelength: 1.064 µm).
Applications:
Fine engraving and micro-cutting.
Medical device manufacturing.
Advantages:
High peak power for pulsed operations.
Suitable for very thin materials.
Limitations:
Lower efficiency compared to fiber lasers.
High operational costs.
2.2 By Machine Configuration
(1) Gantry (Moving Gantry) Laser Cutters
l The laser head moves along X/Y axes over a stationary workpiece.
l Best for: Large-format cutting (sheet metal, signage).

(2) Flying Optic Laser Cutters
The workpiece remains fixed while mirrors/lenses move.
Best for: High-speed cutting of thin materials.
(3) Hybrid Laser Cutters
Combines moving gantry and flying optics.
Best for: Balancing speed and precision.

(4) Robotic Arm Laser Cutters
Uses a multi-axis robotic arm for 3D cutting.
Best for: Automotive and aerospace components.
2.3 By Material Compatibility
| LaserType | Metals | Plastics | Wood | Ceramics | Glass |
| CO₂Laser | Moderate | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Good |
| FiberLaser | Excellent | Poor | Poor | Poor | No |
| Nd:YAGLaser | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | No |
3. Key Technical Parameters
| Parameter | CO₂Laser | FiberLaser | Nd:YAGLaser |
| Wavelength(µm) | 10.6 | 1.06 | 1.064 |
| PowerRange (W) | 25–20,000 | 500–30,000 | 50–6,000 |
| CuttingSpeed | Medium | VeryHigh | Low-Medium |
| Maintenance | High | Low | Medium |
| BestThickness | <20mm | <50mm | <10mm |
4. Industry Applications
Automotive: Precision cutting of chassis components.
Aerospace: Titanium and composite material processing.
Electronics: Micro-cutting circuit boards.
Jewelry: Fine engraving and intricate designs.
5. Conclusion
Laser cutting machines vary significantly in terms of laser source,configuration, and material compatibility. Fiber lasers dominate metal cuttingdue to their efficiency, while CO₂ lasers remain ideal for non-metals. Selectingthe right type depends on material, thickness, precision requirements, andbudget.
For further technical specifications or application-specific recommendations,consult a laser cutting system provider JUGAO CNC MACHINE.