How to choose the best plate rolling machine?
Selecting the optimal plate rolling machine requires a comprehensiveconsideration of your company's production needs, plate characteristics, andbudget. Choosing the most suitable plate rolling machine hinges on consideringthree key factors: what to roll, how to roll, and how much to roll. Below, I'llprovide a detailed analysis of these key points.
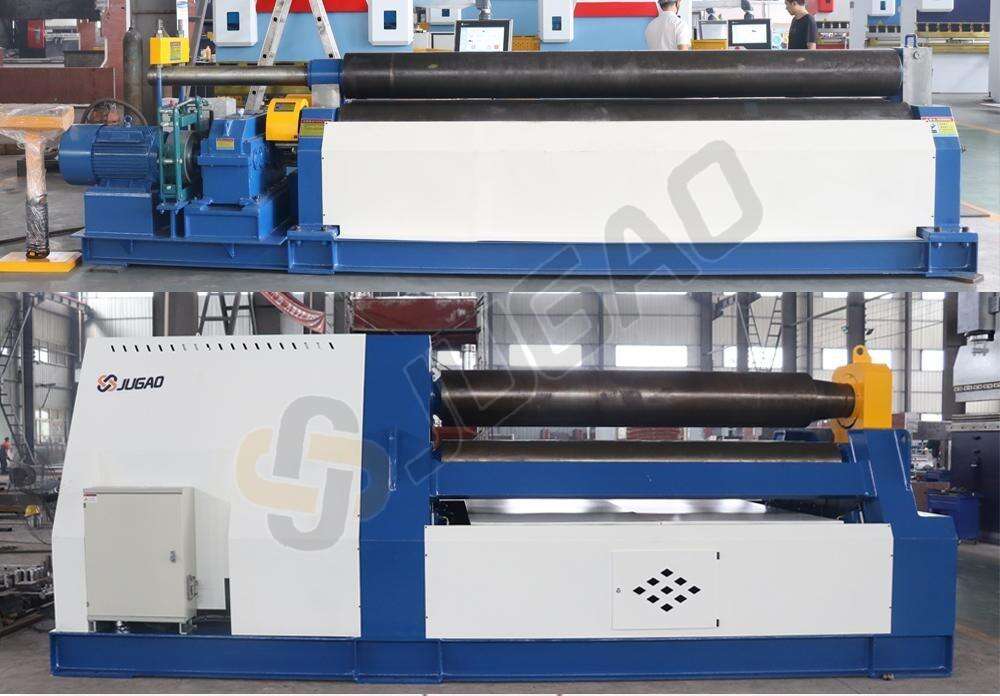

1. Identify processing requirements (most important):
Material type: carbon steel/stainless steel/aluminum alloy (the yieldstrength of different materials influences machine selection and powerrequirements).
Thickness range (thinnest to thickest) and plate width (maximum processingwidth).
Required minimum inner diameter (minimum diameter when rolled intotubes/coils).
Production volume: single piece, high-volume production/small batch,high-mix production/occasional processing (influencing the need for CNC andautomation).
These parameters determine the plate rolling machine's optimal load capacity,drum diameter, and length, among other key specifications.
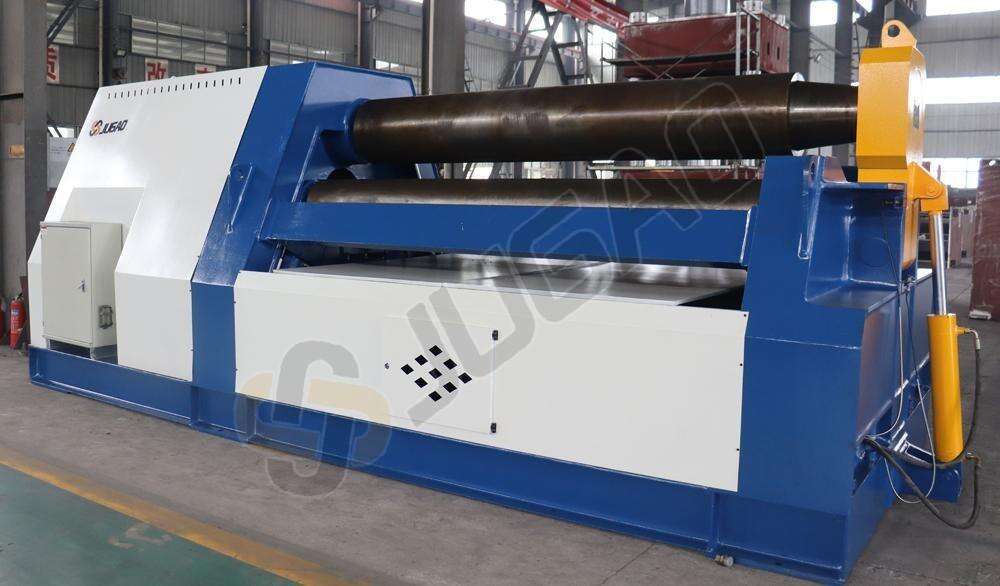

1) Selection Based on Plate Characteristics
– Plate Thickness
Thin plates (1-6 mm): Generally, a three-roller symmetrical plate rollingmachine or a four-roller plate rolling machine is used, offering high precisionand easy adjustment.
Medium and thick plates (6-40 mm): A four-roller plate rolling machine isrecommended, offering easier operation and greater pre-bending capability.
Extra-thick plates (over 40 mm): A heavy-duty four-roller plate rollingmachine or a CNC top-roller universal plate rolling machine is required.
– Plate Width
The working length of the plate roll must be greater than or equal to theplate width; otherwise, processing is impossible.
Common ranges: 1.5 m, 2.5 m, 3.2 m, 4 m, and above.
– Material Strength
Ordinary carbon steel is easy to roll.
High-strength steel and stainless steel require larger, stronger coils.
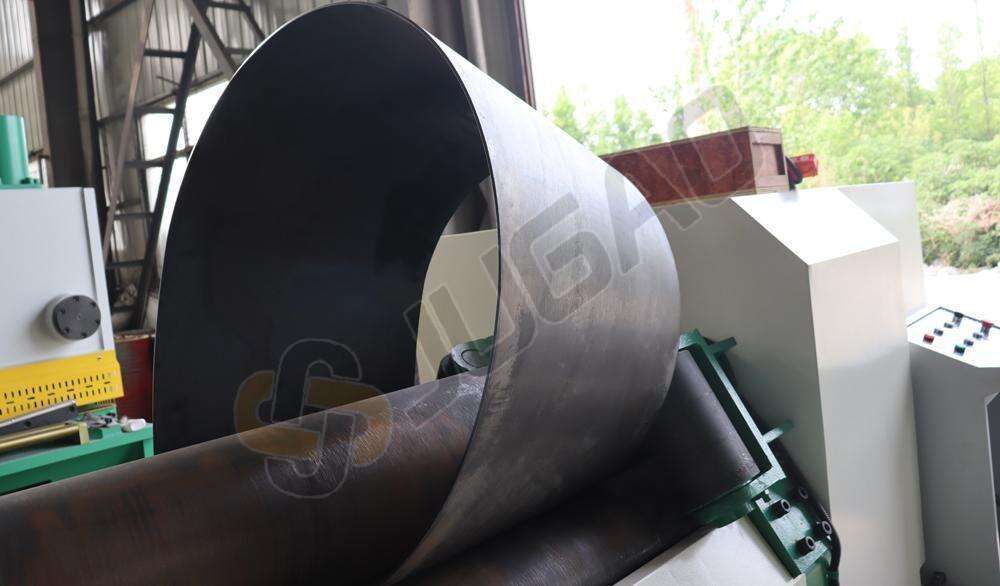

2) Selection Based on Process Requirements
– Forming Accuracy
If high precision and good roundness are required, a four-roller platerolling machine is preferred.
A three-roller symmetrical plate rolling machine requires two workpieceflips, resulting in slightly lower efficiency and accuracy.
– Pre-bending Capability
A three-roller plate rolling machine requires a pre-bending mechanism at theend of the plate or allows for scrap.
A four-roller plate rolling machine has an automatic pre-bending function,which reduces scrap and improves efficiency.
– Conical Forming
If a conical shape is required, a universal plate rolling machine with tiltedside rolls is recommended.
– Automation Level
Manual plate rolling machines are suitable for small batches and lowbudgets.
CNC plate rolling machines are suitable for large batches and automatedproduction lines.
2. Choosing the Optimal Roller Model
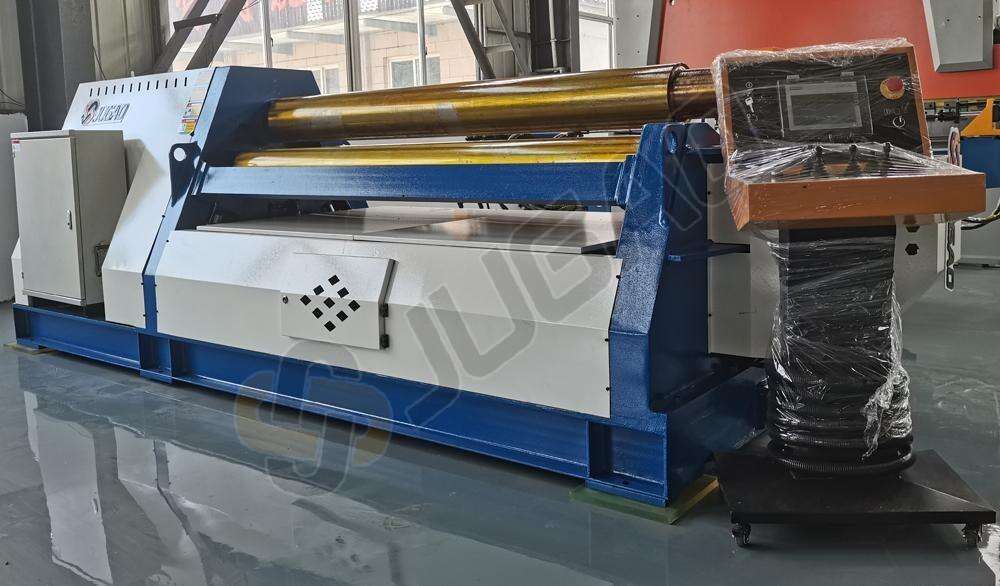

1) Common Plate Rolling Machine Models
Common plate rolling machines include two-roller, three-roller, andfour-roller models (as well as specialized models).
Three-roller: Simple structure and relatively low price. Suitable forgeneral thicknesses and conventional forming, but requires higher operatingskills for small diameters or complex pre-bending processes.
Four-roller (double-press): Utilizing a dual clamping system, front andback clamps, it simplifies operation and facilitates high-precision, small innerdiameter forming. While this reduces labor, it also increases costs.
Two-roller/tapered and specialized machines: Suitable for rolling specialcross-sections or tapered shapes.
The choice between three-roller and four-roller directly impacts pre-bendingefficiency, finished product edge straightness, and minimum coil diameter.
2) Equipment Performance
Roller Diameter and Strength: The larger the roller diameter, the greaterits rigidity and resistance to deformation.
Drive Type: Hydraulic drive > mechanical drive, which offers greaterpower and reliability.
CNC System: Whether or not CNC/PLC control is available influences thelevel of automation and processing efficiency.
Safety and Maintenance: Overload protection, operational safety, and acomplete lubrication system are crucial.
3) Key Technical Parameters
Thickness × Width × Material Yield Strength is the cornerstone of calculatingmachine tool capacity: Manufacturers typically specify machine capacity based ona specific yield strength. If your material is stronger, the actual capacitywill be lower. Please provide the manufacturer with the specific materialinformation for your plate.
A common rule of thumb regarding roller diameter and minimum roller diameteris "maximum roller diameter ≈ 1.5 × top roller diameter." This applies to boththree-roll and four-roll systems. Therefore, if you need to roll smallerdiameter workpieces, you should select smaller top rollers or a more appropriatemachine model.
Roller Length (Effective Working Width): This should at least match yourmaximum plate width, allowing for clamping and pre-bending.
3. Economic and Brand Factors
Budget Range: Domestic plate rolling machines offer highcost-effectiveness. Imported models (such as Italy's DAVI and France's FACCIN)offer high precision and automation, but are more expensive.
After-sales Service: Check local service locations and timely spare partsavailability.
Long-term Investment: Choose energy-efficient, low-maintenance models forgreater long-term profitability.
Recommended Models:
Small sheet metal fabrication plants (light plate) → Three-roll symmetricalor economical four-roll plate rolling machine.
Medium-to-large plants (thick plate, stainless steel) → Hydraulic four-rollplate rolling machine.
High-end manufacturing (pressure vessels, wind power, shipbuilding) → CNCfour-roll or top-roll universal plate rolling machine with automated loading andunloading.

Comparison table of common sheet metal rolling machine models:
| Types | StructuralFeatures | ApplicablePlate Thicknesses | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Three-rollersymmetrical plate roll | Thetop roller can be raised or lowered to accommodate sheet metalturnover. | Thinto Medium Plate (≤20mm) | Smallsheet metal processing, low-cost applications | Simplestructure, low price, and easy maintenance | Cannotbe pre-bent directly, resulting in high scrap rates and lowefficiency. |
| Three-rollerasymmetrical plate roll | Fixedtop roller, lower roller, and adjustable side rollers. | ThinPlate (≤12mm) | Ventilationducts, lightweight metal panels | Partialpre-bending capability, easy operation | Narrowapplication range: cannot process thick plates. |
| Hydraulicthree-roller plate roll | Hydraulicallydriven with large roller shafts. | MediumPlate (20–60mm) | Generalmachinery manufacturing, structural parts | Powerfulpower and high efficiency | Stillrequires a plate end pre-bending machine and workpiece flipping. |
| Four-rollerplate roll | Fourhydraulically driven rollers (upper, lower, left, and right). | Thinto Thick Plate (6–100mm) | Pressurevessels, ships, steel structures | Automaticpre-bending, high precision, high efficiency, and minimal waste | Highprice and complex maintenance. |
| Universaltop-roller plate roll | Universallymovable top roller and tiltable side rollers. | Thickto Extra Thick Plate (40–200mm) | Cones,pressure vessels, wind turbine towers | Capableof rolling cones, suitable for heavy-duty manufacturing | Largeand expensive equipment. |
| CNCplate roll | Equippedwith a CNC/PLC control system. | VariousPlates | High-endmanufacturing, mass production | Highdegree of automation, stable precision, and reduced labor costs | Highcost and requires operator skill. |
Selection Guide:
Limited Budget, Thin Plate Processing → Three-Roller Symmetrical/AsymmetricPlate Rolling Machine
Medium and Thick Plate, High Efficiency Requirements → HydraulicFour-Roller Plate Rolling Machine
Heavy Duty Manufacturing, Special Cones → Top-Roller Universal PlateRolling Machine
High-Volume, High-Precision, Automation Requirements → CNC Four-RollerPlate Rolling Machine
4. Key Points for Plate Rolling Machine Selection
1) Plate Thickness
Thin Plate (≤12mm): Three-roll Asymmetric Plate Rolling
Medium Plate (≤20mm): Three-roll Symmetrical Plate Rolling
Thick Plate (20-60mm): Hydraulic Three-roll/Four-roll Plate Rolling
Extra Thick Plate (≥60mm): Four-roll Plate Rolling/Top-roll Universal PlateRolling
2) Process Requirements
General Rolling: Three-roll
High Precision, Pre-bending, and High Efficiency: Four-roll
Conical Rolling: Conical Plate Rolling
Automation and High Production Requirements: CNC Plate Rolling
3) Budget and Application Considerations
Small Factory with Limited Budget → Three-roll Plate Rolling (HighlyCost-Effective)
Medium to Large Manufacturing Enterprises → Four-roll Hydraulic PlateRolling (Mainstream Choice)
High-end Equipment Manufacturing (Wind Power, Pressure Vessels,Shipbuilding) → CNC Four-roll or Universal Plate Rolling
Choosing the best plate rolling machine means finding the one that best suitsyour working conditions and budget. The best plate rolling machine is not themost expensive one, but the one that best suits your plate thickness, processrequirements and budget.