Introduction à la machine de soudage laser
Le soudage au laser est un procédé polyvalent et précis utilisé pour assembler des composants métalliques dans diverses industries. Cette technique utilise des faisceaux laser concentrés pour fondre et souder les matériaux, créant ainsi des soudures solides et de haute qualité. Les machines de soudage au laser, équipées d'une technologie laser avancée, sont les équipements utilisés pour exécuter ce processus, permettant à la fois une grande précision et une efficacité élevée. Cet article complet explore tous les aspects des machines de soudage au laser, notamment leur fonctionnement, leurs composants, leurs avantages, leurs applications, leurs types, leur maintenance et les tendances futures.
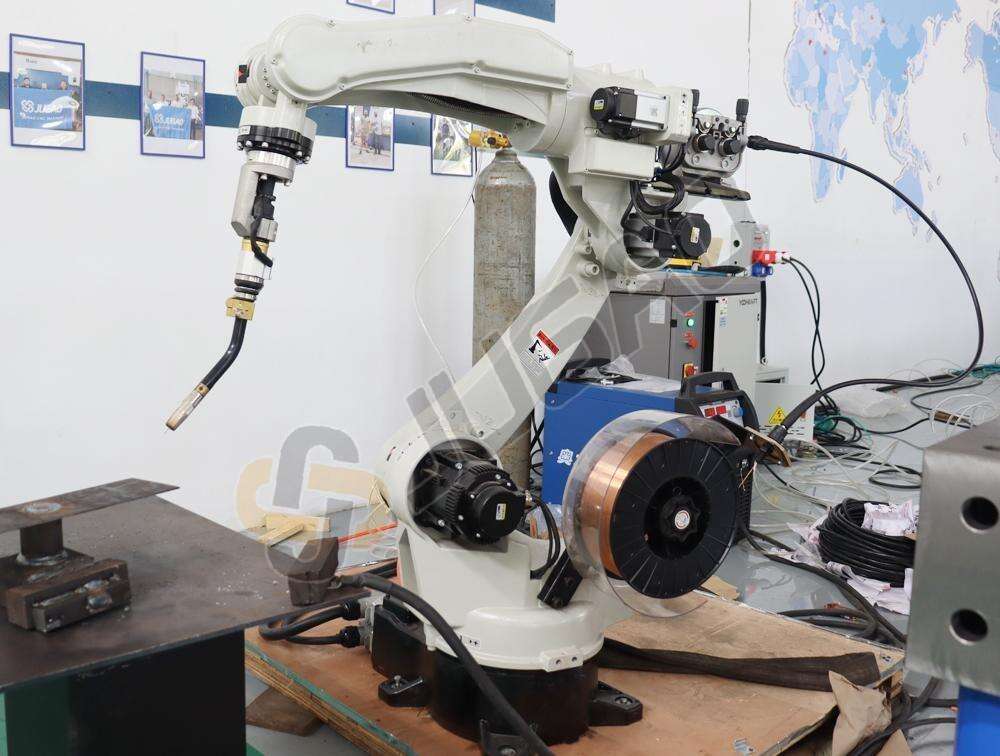

Qu'est-ce qu'une Machine de Soudage Laser ?
Le soudage par laser est un procédé sans contact qui utilise un faisceau laser de haute intensité pour assembler deux matériaux. Le faisceau laser se concentre sur une petite zone, générant suffisamment de chaleur pour faire fondre les matériaux, qui solidifient ensuite en formant un joint solide. Cette technique est réputée pour sa précision, sa rapidité, sa capacité à souder des composants petits et complexes, ainsi que pour sa déformation minimale.
Principe de fonctionnement du soudage par laser
Le soudage par laser est une méthode de soudage utilisant un faisceau laser de haute densité énergétique comme source de chaleur ; son principe comprend principalement les aspects suivants :
Mise au point optique : la machine de soudage par laser génère un faisceau laser à l'aide d'un laser et le focalise à l'aide d'éléments optiques tels que des lentilles ou des miroirs, de sorte que l'énergie laser soit concentrée sur le point de soudure.
Transfert de chaleur : lorsque le faisceau laser atteint la surface de la pièce, l'énergie laser est absorbée et convertie en énergie thermique. La chaleur se propage le long de la partie métallique du joint soudé, ce qui fait augmenter la température du métal.
Fusion et mélange : Lorsque la surface du métal est chauffée à une température suffisamment élevée, le métal commence à fondre et forme un bain liquide. Sous l'effet du faisceau laser, ce bain se propage et se mélange rapidement, permettant ainsi la liaison de l'assemblage métallique.
Refroidissement et solidification : Une fois le faisceau laser arrêté, le bain liquide se refroidit progressivement et un joint soudé se forme durant le processus de solidification. Pendant cette phase, les molécules métalliques se réorganisent et cristallisent pour former un joint soudé solide.
Le soudage laser présente des avantages tels qu'une densité d'énergie élevée, une faible quantité de chaleur introduite, une vitesse de soudage rapide et une zone thermiquement affectée réduite, ce qui le rend particulièrement adapté au soudage de pièces miniatures ou difficiles d'accès.
Composants d'une machine de soudage laser
Source laser
Types de lasers : Les types courants incluent les lasers CO2, les lasers Nd (verre dopé à l'yttrium-aluminium-grenat) et les lasers à fibre. Chaque type présente des avantages spécifiques, en fonction de l'application.
Fonction : La source laser génère le faisceau laser pour le soudage. C'est le composant clé qui détermine la puissance et l'efficacité de la machine.
Optique
Faisceau laser et miroir : Utilisés pour focaliser et diriger le faisceau laser sur la pièce à usiner. Des composants optiques de haute qualité assurent un contrôle précis du faisceau laser.
Système de transmission du faisceau : comprend des composants tels que la fibre optique et le conduit de faisceau qui transfèrent le faisceau laser de la source vers la zone de soudage.
Système de manipulation de la pièce
Table de positionnement : Une plateforme pour placer la pièce. Elle peut être fixe ou équipée d'une fonction mobile afin d'aligner la pièce avec le faisceau laser.
Mécanisme de serrage : permet de maintenir la pièce en place afin d'en empêcher tout déplacement pendant le soudage.
Navar
Commande CNC : Les systèmes de commande numérique par ordinateur (CNC) sont souvent utilisés dans les procédés de soudage automatisés pour contrôler précisément les paramètres de soudage et le déplacement du faisceau laser.
Interface logicielle : Fournit une interface permettant à l'opérateur de saisir les paramètres de soudage et de surveiller le processus.
Passage du liquide de refroidissement
Refroidissement par eau ou par air : Le soudage laser génère beaucoup de chaleur et nécessite un système de refroidissement pour éviter la surchauffe de la source laser et des composants optiques.
Gaine protectrice
Mesures de sécurité : Le boîtier protège l'opérateur contre les rayonnements laser et évacue toute fumée nocive ou débris générés pendant le soudage.
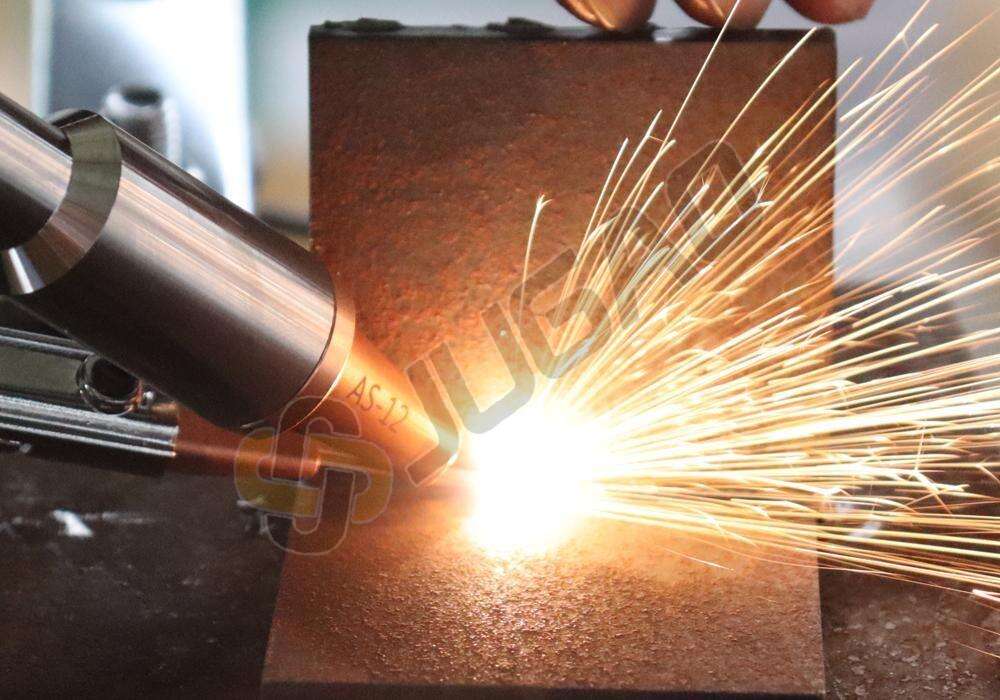

Types de machines de soudage laser
Machines de soudage à la fibre laser
Chirurgie : Utilise une source laser à fibre pour transmettre le faisceau laser à travers la fibre.
Avantages : qualité élevée du faisceau, rendement énergétique élevé, adapté au soudage de divers matériaux.
Machine de soudage laser CO2
Chirurgie : Une source excimère CO2 est utilisée pour générer un faisceau laser en stimulant électriquement un mélange gazeux.
Avantages : puissance élevée et capacité à souder des matériaux épais.
Machine de soudage par faisceau laser ND
Chirurgie : En utilisant une source d'excitation ND, un faisceau laser est produit en dopant du néodyme dans un cristal de grenat d'aluminium et d'yttrium.
Avantages : Puissance crête élevée, adapté aux applications de soudage par impulsions.
Machine de soudage au laser à diode
Chirurgie : Une source laser à diode est utilisée pour générer un faisceau laser à travers une diode semi-conductrice.
Avantages : petite taille, économie d'énergie, peut souder des pièces de petite taille et de précision.
Avantages et inconvénients de la machine de soudage au laser
Avantages de la machine de soudage laser
Les machines de soudage au laser présentent de nombreux avantages et conviennent parfaitement à diverses applications industrielles. Ces avantages incluent la précision, la rapidité, la polyvalence et la qualité globale. Voici un aperçu détaillé des avantages des machines de soudage au laser :
Précision et exactitude
Tolérances strictes : Les machines de soudage au laser peuvent atteindre des tolérances extrêmement strictes, ce qui est essentiel pour les applications nécessitant une haute précision.
Zone affectée par la chaleur (ZAC) réduite : Le faisceau laser est fortement focalisé, créant une petite zone affectée par la chaleur. Cela minimise la déformation thermique et réduit le risque d'endommager les matériaux adjacents.
Le soudage est rapide
Amélioration de la productivité : Le soudage laser peut être effectué à grande vitesse, ce qui améliore considérablement la productivité et réduit le temps de cycle.
Fonctionnalités d'automatisation : Le processus peut être facilement automatisé à l'aide d'un système CNC et de robots, ce qui améliore encore la rapidité et la régularité.
Polyvalence
Compatibilité des matériaux : le soudage laser est compatible avec une variété de matériaux, y compris divers métaux (acier, aluminium, titane, etc.), alliages et même certains plastiques.
Géométrie complexe : Ce procédé permet de souder des géométries complexes difficiles à réaliser avec les méthodes de soudage traditionnelles.
Qualité de soudage excellente
Soudures solides : Le soudage laser peut produire des soudures de haute résistance, dotées d'excellentes propriétés mécaniques, garantissant durabilité et fiabilité.
Soudures propres et esthétiques : Les soudures sont généralement propres et esthétiques, nécessitant seulement une finition mineure. Cela est particulièrement important pour les applications où l'apparence est critique, comme dans les industries automobile et de la bijouterie.
Distorsion minimale
Réduction des contraintes thermiques : les sources de chaleur concentrées permettent de minimiser les contraintes thermiques et les déformations, préservant ainsi l'intégrité de la pièce.
Contrôle précis : Le laser peut être contrôlé avec précision afin de produire une déformation minimale des matériaux minces.
Flexibilité
Procédé sans contact : Le soudage au laser est un procédé sans contact, ce qui signifie qu'il n'y a pas de contact physique entre l'outil et la pièce. Cela réduit l'usure de l'équipement et permet le soudage dans des zones difficiles d'accès.
Paramètres réglables : Les paramètres du processus (puissance du laser, vitesse, focalisation, etc.) peuvent être facilement ajustés pour s'adapter à différents matériaux et épaisseurs.
Efficacité énergétique
Utilisation efficace de l'énergie : Les machines de soudage laser, en particulier celles utilisant des lasers à fibre, sont très économes en énergie. Elles transforment une grande partie de l'électricité en faisceau laser.
Réduction des coûts d'exploitation : À long terme, l'efficacité énergétique se traduit par des coûts d'exploitation plus faibles.
Automatisation et intégration
Intégration transparente : Le système de soudage laser peut être intégré sans heurts dans la ligne de production automatisée, ce qui améliore l'efficacité globale de la fabrication.
Soudage robotisé : La précision et le contrôle offerts par le soudage laser en font un choix idéal pour les applications de soudage robotisé, permettant un fonctionnement continu et une haute productivité.
Réduction des matériaux consommables
Consommables minimes utilisés : Contrairement aux méthodes de soudage traditionnelles qui nécessitent des matériaux d'apport et des électrodes, le soudage laser requiert généralement peu ou pas de consommables.
Économies de coûts : La réduction de l'utilisation de consommables permet de réaliser des économies et diminue la nécessité de réapprovisionnement.
Amélioration de la sécurité et de la propreté
Fonctions de sécurité : Les machines modernes de soudage laser sont équipées de fonctions de sécurité telles qu'un boîtier de protection et un dispositif de verrouillage afin de protéger les opérateurs contre les rayonnements laser nocifs.
Procédé de nettoyage : Par rapport aux méthodes de soudage traditionnelles, ce procédé produit moins de fumée et d'éclaboussures, ce qui donne un environnement de travail plus propre.
Bénéfice environnemental
Respectueux de l'environnement : L'efficacité et la précision du soudage laser réduisent les déchets et la consommation d'énergie, ce qui en fait un choix respectueux de l'environnement.
Fabrication durable : Le soudage laser soutient les pratiques de fabrication durable en minimisant les déchets de matériaux et en améliorant l'efficacité énergétique.
Inconvénients des machines de soudage laser
Bien que les machines de soudage laser présentent de nombreux avantages, elles comportent également certains inconvénients à prendre en compte. Voici quelques-uns des principaux inconvénients des machines de soudage laser :
Des coûts initiaux élevés
Machines coûteuses : Les machines de soudage laser sont souvent plus chères que les équipements de soudage traditionnels en raison de leur technologie avancée et de leurs composants.
Coût des sources laser : Les sources laser de haute qualité, telles que les lasers à fibre et les lasers ND, augmenteront le coût global.
Installation complexe : La mise en place d'un système de soudage laser peut être complexe et nécessite une expertise.
Exigences d'infrastructure : L'installation peut nécessiter une infrastructure supplémentaire, telle que des systèmes de refroidissement, des enceintes de protection et des systèmes de ventilation avancés.
Complexité technique
Formation professionnelle : Les opérateurs doivent suivre une formation spécialisée pour utiliser et programmer les machines de soudage laser.
Programmation complexe : La configuration et la programmation d'un système de commande numérique (CNC) peuvent être complexes et nécessitent une expertise en logiciels CAO/FAO et en paramètres de soudage.
Expertise en maintenance : La maintenance des machines de soudage laser requiert de l'expertise et des compétences.
Étalonnage périodique : Afin de maintenir la précision, un étalonnage fréquent et un réglage du système laser sont nécessaires.
Sensibilité de la préparation et de l'assemblage des connecteurs
Préparation du joint : Le soudage laser nécessite une préparation et un alignement précis des joints. Même de petites déviations peuvent entraîner une mauvaise qualité de soudage.
Tolérance coopérative : Le procédé présente une faible tolérance aux jeux et aux désalignements, ce qui exige un fixation et un positionnement précis.
Limitations sur l'épaisseur du matériau
Limitations sur la plage d'épaisseur : Le soudage laser est plus adapté aux matériaux de faible à moyenne épaisseur. Le soudage de matériaux très épais peut nécessiter plusieurs passes ou un préchauffage.
Dissipation de la chaleur : Pour les matériaux plus épais, la gestion de la dissipation thermique devient plus difficile, ce qui peut affecter la qualité du soudage.
Problème de sécurité
Risque d'exposition : Il existe un risque d'exposition aux rayonnements laser nocifs provenant du soudage laser, pouvant causer des dommages graves aux yeux et à la peau.
Mesures de protection : Des mesures de sécurité complètes telles qu'un boîtier de protection, des lunettes de protection et des protocoles de sécurité laser sont essentielles.
Fumées nocives : Le procédé produit des fumées nocives et des particules, nécessitant des systèmes efficaces de ventilation et d'extraction des fumées.
Débris : Les faisceaux laser de haute intensité peuvent produire des débris et des projections, ce qui peut entraîner des risques supplémentaires pour la sécurité.
La compatibilité des matériaux est limitée
Problème de réflectivité : Les matériaux à forte réflectivité, tels que l'aluminium et le cuivre, peuvent réfléchir les faisceaux laser, rendant le soudage plus difficile et moins efficace.
Revêtement spécial : Un revêtement spécial ou un traitement de surface peut être nécessaire pour améliorer la soudabilité du matériau réfléchissant.
Sensibilité aux alliages : Certains alliages peuvent présenter des défis spécifiques en matière de soudage laser liés aux fissures, à la porosité ou à des changements métallurgiques.
Bien que les machines de soudage laser offrent des avantages significatifs en termes de précision, de vitesse et de polyvalence, elles présentent également plusieurs inconvénients. Les principaux inconvénients incluent des coûts initiaux élevés, une complexité technique, une sensibilité à la préparation des joints et des préoccupations en matière de sécurité. De plus, lors de la mise en œuvre de la technologie de soudage laser, des facteurs tels que les limitations liées à l'épaisseur des matériaux, les problèmes de compatibilité et les exigences environnementales doivent être soigneusement pris en compte.
Application de la machine à soudage laser
Industrie automobile
Soudage de composants : utilisé pour souder des pièces moteur, des pièces de boîte de vitesses, le système d'échappement et d'autres pièces automobiles.
Structure de carrosserie : la carrosserie de la voiture est soudée au laser afin d'obtenir un assemblage solide et léger.
Industrie aérospatiale
Composants aéronautiques : utilisé pour souder des composants critiques d'aéronefs, notamment les pales de turbine, les réservoirs de carburant et les éléments structurels.
Précision : la haute précision du soudage laser garantit l'intégrité et les performances des composants aérospatiaux.
Industrie électronique
Micro-soudage : Le soudage au laser est idéal pour les applications de micro-soudage dans le domaine électronique, comme la connexion de fils fins et l'assemblage de composants de précision.
Fabrication de batteries : utilisé pour la production de batteries afin d'assurer une connexion solide et fiable.
Industrie des dispositifs médicaux
Implants et instruments : Le soudage au laser est utilisé pour la fabrication d'implants médicaux et d'instruments chirurgicaux, offrant des soudures précises et propres.
Biocompatibilité : Le procédé garantit que le cordon de soudure est biocompatible et répond aux normes médicales strictes.
Joaillerie et horlogerie
Soudage fin : Le soudage au laser est utilisé pour des applications de soudage fin en joaillerie et en horlogerie, permettant des conceptions complexes et des réparations délicates.
Qualité esthétique : produit un soudage de haute qualité, améliorant la beauté des bijoux et des montres.
Industrie de l'Énergie
Panneaux solaires : Utilisé dans la fabrication de panneaux solaires pour assurer des connexions durables et efficaces.
Éoliennes : Le soudage au laser est utilisé pour fabriquer des composants d'éoliennes, offrant un assemblage solide et fiable.
Fonctionnement de la machine de soudage au laser
Établir
Préparation : nettoyer la pièce et effectuer les préparations de soudage afin d'assurer une bonne qualité de soudure.
Positionnement : placer la pièce sur la table de positionnement et la fixer à l'aide d'un outillage.

Programmation
Saisie des paramètres : l'opérateur saisit dans le système de contrôle des paramètres spécifiques de soudage tels que la puissance du laser, la vitesse, la durée de l'impulsion et la position du foyer.
Programmation du trajet : les trajectoires de soudage sont généralement programmées à l'aide d'un logiciel CAO/FAO afin de guider le faisceau laser le long du cordon de soudure souhaité.
Procédure de soudage
Génération du faisceau : la source d'excitation génère un faisceau laser qui irradie la zone de soudage à travers des éléments optiques.
Fusion et fusionnement : un faisceau laser focalisé fait fondre le matériau au niveau du joint, formant un bain de matière en fusion qui se solidifie pour constituer la soudure.
Contrôle du déplacement : le système CNC contrôle le déplacement du faisceau laser et/ou de la pièce afin de suivre le trajet de soudage programmé.
Après soudage
Refroidissement : après le soudage, laisser refroidir complètement le joint jusqu'à sa pleine solidification.
Vérification : Vérifiez la qualité de la soudure, vérifiez s'il y a des porosités, des fissures ou des défauts de fusion incomplète.
Maintenance de la machine de soudage laser
Nettoyage régulier
Optique : Nettoyez les lentilles, les miroirs et autres composants optiques afin d'assurer une qualité optimale du faisceau laser.
Zone de travail : Gardez la zone de travail propre et exempte de débris afin d'éviter toute contamination du faisceau laser et de la pièce.
Entretien du système de refroidissement
Vérifiez le niveau de liquide de refroidissement : Vérifiez et rechargez régulièrement le liquide de refroidissement afin d'éviter la surchauffe de la source laser et des composants optiques.
Vérifiez le système de refroidissement : Vérifiez l'absence de fuites dans le système de refroidissement et assurez-vous qu'il fonctionne correctement.
Étalonnage et alignement
Étalonnage du laser : La source laser est étalonnée régulièrement afin d'assurer une puissance et une qualité de faisceau correctes.
Alignement optique : Vérifiez et ajustez l'alignement des éléments optiques afin de maintenir une transmission précise du faisceau.
Mise à jour logicielle
Mise à jour du logiciel de commande : Tenez à jour le logiciel de commande CNC afin d'accéder aux dernières fonctionnalités et améliorations.
Programme de sauvegarde : Le programme de soudage est régulièrement sauvegardé afin d'éviter toute perte de données et garantir une récupération rapide en cas de problème logiciel.
Tendances futures du soudage laser
Progrès dans la Technologie Laser
Lasers de puissance accrue : Développer des sources laser plus puissantes pour souder des matériaux plus épais et plus difficiles.
Amélioration de la qualité du faisceau : Les progrès de la technologie laser ont amélioré la qualité et la précision du faisceau.
Intégration dans l'industrie 4.0
Connexion à l'Internet des objets : Intégration de l'Internet des objets (IdO) pour la surveillance et le contrôle en temps réel du processus de soudage laser.
Analyse des données : Utiliser l'analyse des données pour optimiser les paramètres de soudage et améliorer la qualité et l'efficacité.
Automatisation et robotique
Intégration de robots : Les systèmes robotisés sont de plus en plus utilisés pour le soudage laser automatisé afin de réduire la main-d'œuvre manuelle et accroître la productivité.
Robots collaboratifs : Développer des robots collaboratifs (cobots) capables de travailler aux côtés d'opérateurs humains dans des applications de soudage laser.
Développement durable
Efficacité énergétique : Continuer à améliorer l'efficacité énergétique des machines de soudage laser afin de réduire leur impact environnemental.
Fabrication verte : L'utilisation de pratiques de fabrication durables, incluant l'usage de matériaux et de procédés respectueux de l'environnement.

Conclusion
Les machines de soudage au laser sont la pierre angulaire de la fabrication moderne, réputées pour leur précision, leur rapidité et leur polyvalence dans l'assemblage de composants métalliques. Leur technologie avancée et leurs capacités d'automatisation les ont rendues indispensables dans des secteurs tels que l'automobile, l'aérospatiale, l'électronique et l'équipement médical. Grâce à un entretien adéquat et en s'alignant sur les tendances émergentes, ces machines peuvent continuer à répondre aux exigences en constante évolution de la fabrication. À mesure que la technologie progresse, le soudage au laser est appelé à jouer un rôle de plus en plus essentiel dans la définition de l'avenir de la production industrielle.