Comprehensive analysis of press brake: core technical equipment in the field of metal forming
The core value and working principle of press brake
The plasticity of metal materials makes it the basic material of modernindustry, and the press brake is the key equipment to achieve precision formingby using this characteristic. As the core equipment in the field of sheet metalprocessing, the press brake transforms flat metal into various complex geometricshapes by precisely controlling the deformation process, meeting a wide range ofmanufacturing needs from aerospace to daily household appliances.
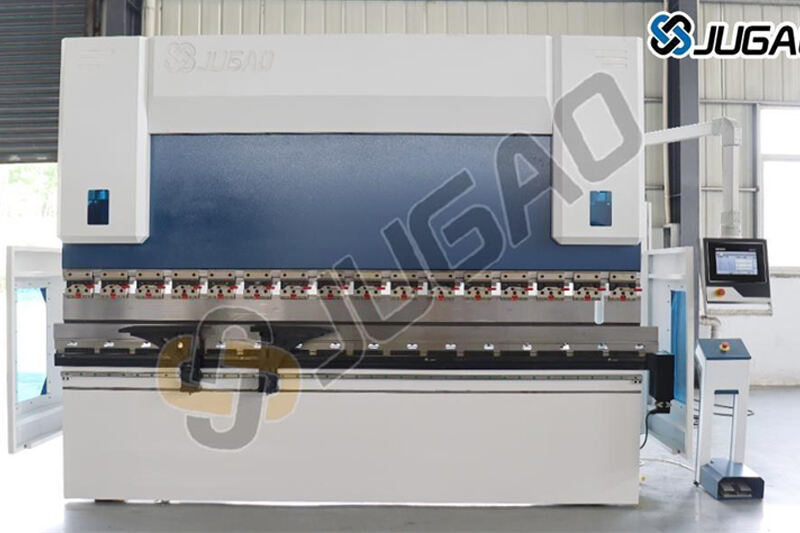

Press Brake is an industrial equipment used for cold forming of metal sheets.It applies controllable pressure to make the metal sheet produce plasticdeformation at a predetermined position to obtain the required angle and shape.As the core equipment in the field of sheet metal processing, the press brakecan complete various processing needs from simple single bending to complexmulti-pass forming.
Origin of equipment naming and technological evolution
The professional term "Press Brake" combines two key concepts:
Press: Derived from the Latin word "pressare", it refers to a mechanicaldevice that applies pressure
Brake: In Old English, it means a pressing tool and has been used todescribe forming equipment since the 14th century
Modern press brakes have developed into high-precision processing systemsthat integrate mechanical, hydraulic, electrical and CNC technologies. Itstechnological evolution has undergone a revolutionary leap from manualmechanical to fully automatic CNC control.
Technical classification and performance comparison of modern pressbrakes
Comparison of mainstream drive technologies
| Type | Typicaltonnage range | Repeatability | Workingspeed | Energyefficiency | Applicablescenarios |
| Hydraulicdrive | 30-6000tons | ±0.05mm | Medium | Medium | Heavy-dutyprocessing of thick plates |
| Servoelectric | 10-300tons | ±0.01mm | High | High | Precisionthin plate forming |
| Pneumatic | 5-100tons | ±0.1mm | High | High | Lightweightrapid prototyping |
| Mechanical | 20-500tons | ±0.2mm | Low | Low | Traditionalmass production |
Classification by control system
| Type | Numberof controlled axes | Positioningaccuracy | Features | Applicablescenarios |
| OrdinaryNC | 2-3axes | ±0.1mm | Simpleprogramming | Massproduction of standard parts |
| EconomicalCNC | 4-6axes | ±0.05mm | Graphicalinterface | Smallbatches of multiple varieties |
| Full-functionCNC | 8-12axes | ±0.01mm | 3Dsimulation/adaptive control | Complexsurface forming |
| Intelligentbending center | 12+axes | ±0.005mm | AIprocess optimization/IoT connection | Digitalfactory |
Analysis of core technical parameters
Nominal force (Tonnage): determines the thickness of the processablematerial, calculation formula: T=(K×S×L×σb)/1000
(K: safety factor 1.2-1.5, S: plate thickness mm, L: bending length mm, σb:material tensile strength MPa)
Workbench length: standard specifications range from 1m to 12m, determinesthe maximum processing width
Opening height: affects the workpiece height and mold size selection
Deflection compensation system: key technology to ensure the straightnessof long workpiece bending
Key components and technical analysis
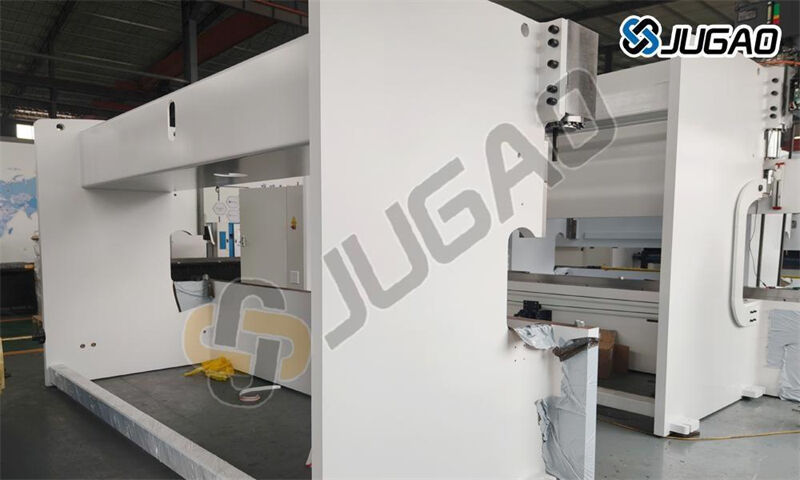
Frame structure
Integral welding: C-type/O-type frame, high rigidity
Stress relief process: vibration aging treatment (eliminating more than 95%of residual stress)
Finite element optimization: workbench deflection <0.02mm/m

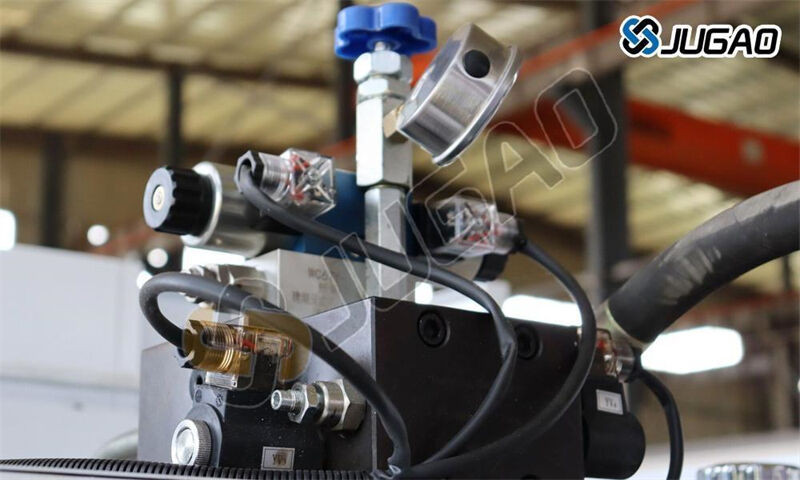
Hydraulic system
Advanced configuration:
Proportional servo valve (response time <10ms)
Accumulator group (instantaneous flow compensation)
Oil temperature control system (maintaining 40±2℃)
Energy-saving technology:
Variable displacement pump (energy saving 30%)
Pressure matching control

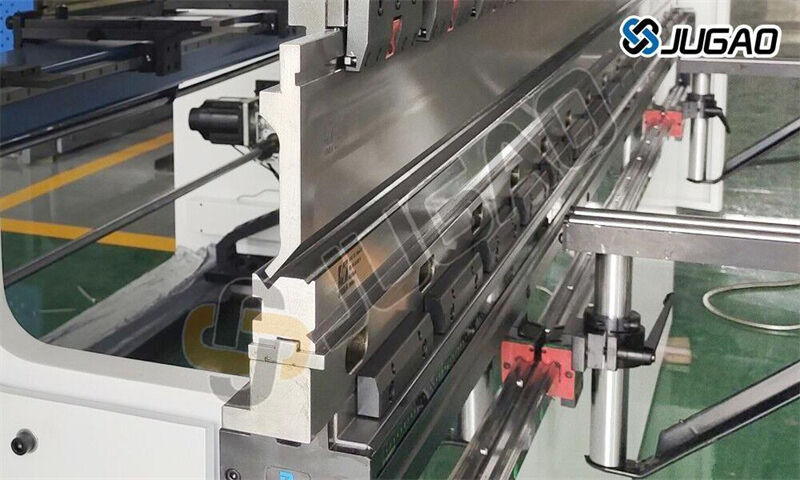
Mold system
Material standards:
Upper mold: 42CrMo (hardness HRC52-54)
Lower mold: Cr12MoV (hardness HRC58-60)
Geometric parameters:
V-groove width = 6×material thickness (general rule)
Tip radius R = 0.2-0.6×material thickness

Forming process
Air bending: the most commonly used method, the forming angle is determinedby the lower die V-mouth and the pressing depth
Bottom pressure bending: high-precision forming, requiring precise controlof pressure and position
Progressive bending: complex polygonal forming process
Rolling bending: special technology for large arc forming
Equipment life cycle management
Preventive maintenance system
Daily inspection: 8 key parameter monitoring (oilpressure/temperature/cleanliness, etc.)
Quarterly maintenance: hydraulic oil particle size detection (NAS 8-levelstandard)
Annual overhaul: guide rail precision calibration and seal replacement
Intelligent maintenance solution
Vibration monitoring system (predict bearing life)
Online oil analysis (water/acid value/contamination)
Remote diagnosis platform (5G technology support)
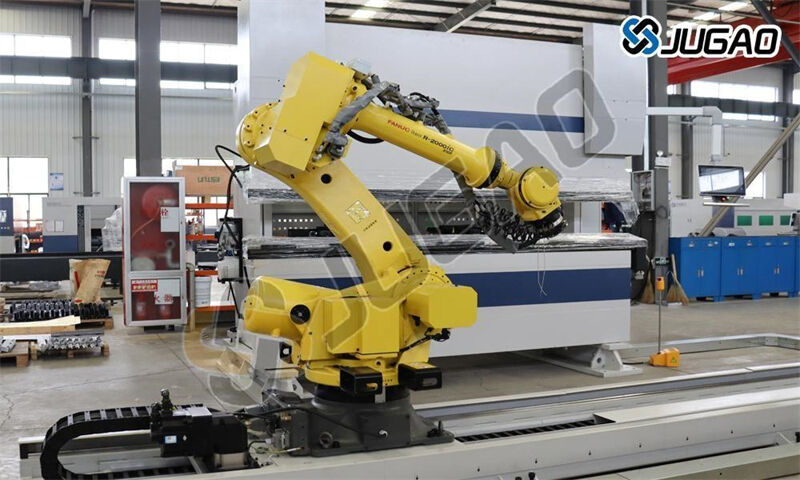
Technology development trends and innovation directions
Frontier technology application
1. Adaptive control: real-time process adjustment based on materialproperties
2. Human-machine collaboration: safe area monitoring and guidanceassistance
3. Green manufacturing: oil mist recovery efficiency >99%
4. Digital main line: full data connection from design to service

JUGAO press brake represents the highest technical level of current metalforming equipment. Its innovative design not only meets the currentmanufacturing needs, but also provides reliable basic equipment for theconstruction of smart factories in the era of Industry 4.0. Choosing a suitablebending solution will significantly enhance the manufacturing capabilities andmarket competitiveness of the enterprise.