Sumary of common press brake failure analysis

1. The main motor cannot start
Reason
1. Fault in the main motor starting circuit, such as: emergency stop button not released, loose cable connection, 24V control power supply, etc.;
2. Fault in related components of the main motor starting part, such as: overload protection or damage of thermal relays, circuit breakers, AC contactors, etc.;
3. Power supply problem;
Measures
1. Check whether the main motor starting circuit has emergency stop not released, loose wiring, and 24V control power supply;
2. Check whether the components of the main motor starting circuit have overload protection. If there is a need to analyze the cause, check whether there is any component damage;
3. Check whether the three-phase power supply is normal;

2. The slider cannot move down quickly
Reasons
1. The slider rail is adjusted too tight;
2. The rear stop shaft is not in place;
3. The slider is no longer at the top dead center;
4. The foot switch and other signals have not entered the module;
5. The proportional servo valve is faulty;

Measures
1. Check whether the slider rail is suitable;
2. Check whether there is a cursor at the actual X position on the system, or check whether the programmed value of the rear stop shaft is consistent with the actual value in the manual interface;
3. The Y-axis status on the system should be "1". If it is "6", check the actual coordinates of the Y-axis. The value should be less than the difference between the Y-axis and the return stroke;
4. According to the electrical schematic, check whether the input signals such as the foot switch are normal;
5. Check whether the feedback of the proportional servo valve is normal;
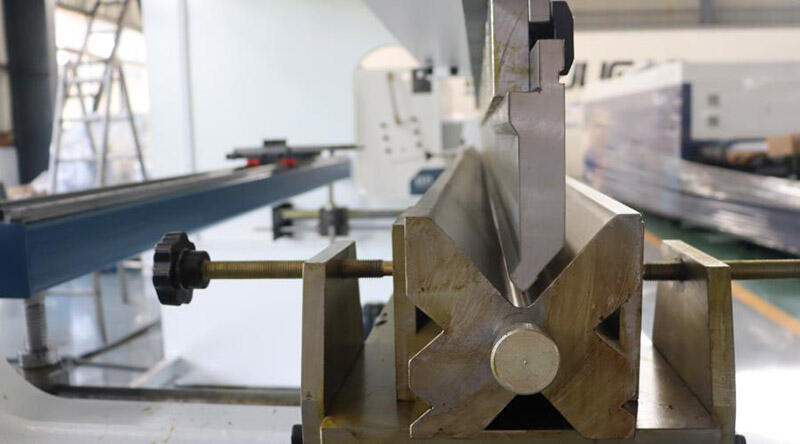
3. The slider cannot bend or the bending speed is very slow
Reason
1. The slider has not reached the speed conversion point;
2. The system Y-axis bending parameters are not set properly;
3. Insufficient pressure, such as: programming operation reasons, machine tool parameter setting reasons, hydraulic reasons, etc.;

Measures
1. Check whether the Y-axis state changes from "2" to "3". The actual value of the Y-axis should be greater than the speed conversion point value. If not, the fast-forward parameters need to be adjusted;
2. Re-adjust the Y-axis bending parameters;
3. Check whether it is due to programming operation, parameter setting, or hydraulic reasons; you can use a pressure gauge, multimeter, etc. to first detect the signals of the main pressure and proportional pressure valve, then check whether the proportional pressure valve and the main pressure reducing valve are stuck, then check the filter element and oil, and finally check the oil pump and its coupling;
4. The slider sometimes cannot return when bending
Reason
1. Failure to return when unloaded may be due to parameter problems or hydraulic failure;
2. Failure to return during processing, the workpiece angle has not reached the set value;
3. Failure to return during processing, the workpiece angle has exceeded the set value;

Measures
1. Debug some parameters of the Y-axis bending. The bending parameters should be debugged according to the actual situation. If the gain is too small, the slider will not be able to bend or not bend in place. If the gain is too large, the slider will shake. The parameters should be adjusted so that the slider does not shake during action and the gain is as large as possible; or the left and right valve offsets in the diagnostic program are not set well. If the Y-axis is too small, it cannot be in place. If the Y-axis is too large, it cannot unload; if It is a hydraulic failure. You need to check the main pressure and check whether the PV valve S5 is always in the energized position;
2. The parameter gain of the Y-axis bending part may be set too small, which can be increased appropriately; or the pressure is insufficient. Analyze the reason for the insufficient pressure, whether it is programming or signal or hydraulic reasons; programming reasons mainly include mold selection, plate thickness, material, workpiece length, bending method, etc., hydraulic reasons mainly include whether the oil pump has internal leakage, whether the proportional pressure valve is contaminated or damaged, whether the filter element is blocked, whether the oil has been contaminated, etc.;
3. It is mainly programming and operation reasons. Check the programmed and processed workpieces;
5. The slider does not move well
Reasons
1. The slider rail is not tight enough;
2. The slider locking nut is loose;
3. The machine tool parameters need to be adjusted;
4. The gain and zero position on the proportional servo valve amplifier need to be adjusted;
5. The back pressure valve pressure is set incorrectly or the two sides are unbalanced. If the back pressure is set too small, the slider will slide down slowly and shake during operation; if the back pressure is unbalanced on both sides, the slider will twist during operation;
Measures
1. Re-adjust the guide rail clearance;
2. Re-tighten. If the locking nut and the screw are too loose, they need to be replaced;
3. If there is a reference curve, it should be adjusted according to the reference curve;
4. Only BOSCH and REXROTH valves are adjustable, but be careful;
5. Use a pressure gauge to adjust the back pressure valve pressure and make it consistent on both sides;

6. Sometimes the main motor stops automatically, and the thermal relay and circuit breaker are protected
Reasons
1. The proportional pressure valve and the main pressure reducing valve are stuck, and the machine tool has been in a pressurized state;
2. The filter element is blocked, the oil flow is not smooth, and the oil pump pressure is always high;
3. The oil has been used for too long and has been contaminated;
4. The oil quality is too poor;
5. The circuit breaker and thermal relay have problems, and they operate when the rated current is not reached;
6. The system control pressure output part is faulty, sending out wrong signals, so that the proportional pressure valve keeps working;

Measures
1. Clean the proportional pressure valve and the main pressure reducing valve;
2. Replace the filter element and check the degree of oil contamination;
3. Replace the oil filter element immediately;
4. Replace with the recommended oil;
5. Replace the circuit breaker and thermal relay;
6. Check the system output;
7. Any valve is stuck
Reason
1. The oil has been used for too long and has been contaminated;
2. The oil quality is too poor;
3. Check whether the rubber skin of the oil inlet in the oil tank is aged;

Measures
1. It is recommended that customers replace the oil on time;
2. Replace the recommended oil;
3. Replace the oil-resistant rubber sheet;
8. Oil cylinder slides down
Reasons
1. The back pressure valve and poppet valve are dirty or damaged;
2. The back pressure is low;
3. The grid ring is strained or worn;
4. The inner wall of the oil cylinder is strained;
5. If the slider stops at any position and slides down slowly, and the slide is less than 0.50mm in 5 minutes, it is normal. This phenomenon is mainly caused by the characteristics of hydraulic oil;

Measures
1. Clean the back pressure valve and poppet valve, and replace them if damaged;
2. Readjust the back pressure valve pressure according to the standard;
3. Replace the grid ring and check the reasons for the grid ring strain and wear;
4. Generally caused by oil contamination, replace the cylinder barrel and sealing ring;
5. No treatment is required;
9. When pressing the mold, the heights on both sides are inconsistent
Reason
1. The back pressure on both sides is inconsistent, and the back pressure setting may be too high;

Measures
1. Adjust the back pressure on both sides to the specified value and keep it consistent;
10. The waiting time at the speed conversion point when the slider is working is too long
Reason
1. The oil suction port in the oil tank is leaking;
2. The filling valve is faulty, such as improper installation causing the valve core to get stuck, or insufficient spring tension;
3. The Y-axis working parameters are not set properly;

Measures
1. Check the seal of the rubber plate and reinstall the cover here;
2. Check the installation of the filling valve, check the valve core movement, and check the spring tension;
3. Adjust the Y-axis working parameters;
11. The length and angle of the workpiece change too much during bending
Reason
1. The machine tool inertia parameter setting is not appropriate;
2. The material of the processed plate;
Measures
1. Re-adjust the machine tool inertia parameter;
2. Check the material of the plate;
12. When the workpiece has multiple bends, the dimensional error of the cumulative error is too large
Reason
1. The workpiece has many bends, resulting in large cumulative errors;
2. The bending sequence is unreasonable;
Measures
1. Fine-tune the accuracy of each bend to make the angle as negative as possible and the size as accurate as possible;
2. Adjust the bending sequence if possible;

13. The pressure automatically calculated by the system is greater than the mold impedance
Reason
1. The lower mold selection is unreasonable during programming;
2. The mold impedance setting is incorrect;
3. The bending method is incorrectly selected during programming;
4. The parameters of the machine tool constants are modified, such as material parameters, unit selection and other parameters;
Measures
1. The mold should be selected according to the relationship between the plate thickness and the lower mold opening;
2. Correctly set the mold impedance;
3. Check the program;
4. Check the machine tool constant parameters;
14. When programming large arc bending, the system calculates very slowly or freezes
Reason
1. The X value set during programming exceeds the maximum value of the X axis in the parameters;
Measure
1. Check the program;
15. The oil temperature is too high
Reason
1. Hydraulic part failure, such as filter element blocked, oil contamination, deterioration, etc.;
2. Long-term high-pressure operation;

Measure
1. Check the filter element and oil, and replace them if necessary;
2. Check the reason for long-term high-pressure operation, whether it is actual need or other reasons;
16. The angle of the processed workpiece is inaccurate
Reason
1. If the error is very large, it may be a programming error, a loose slider connection, a grating ruler failure, etc.;
2. It is normal to have a little error, which can be corrected on the system. If it can work stably after correction, it is normal;
3. The angle is unstable and often changes, which may be related to the loose slider connection, grating ruler failure, material quality, etc.;
Measures
1. Check the running program, focusing on whether the mold, material, plate thickness, workpiece length, bending method in the program are consistent with the actual operation, whether the slider connection is loose, and whether the grating ruler connection is firm;
2. It is normal to have a little error, which may be caused by many reasons, such as: the error between the programmed material thickness and the actual thickness used; material uniformity, mold wear, operation, etc.;
3. Check the Y-axis repeat positioning accuracy, check whether the slider connection and grating ruler connection are normal. If normal, it is likely to be related to the material Material related;

17. Inaccurate size of workpiece
Reason
1. The size is unstable and changes frequently, which may be related to factors such as machine power supply, servo drive, servo motor encoder and related cables, systems, screw mechanical connections, synchronous belts (wheels), etc.;

2. The size has deviations, but is stable, which is mostly related to the parallelism, straightness, parallelism and verticality of the back gauge beam;

3. When positioning with the bending edge, the bend angle is greater than 90 degrees, resulting in smaller size;
Measures
1. Check the repeat positioning accuracy of the back gauge shaft, which is generally less than 0.02mm. If the difference is large, it is necessary to check the possible factors one by one. If it is caused by the servo drive, servo motor encoder, system, etc., it is best to be handled by the manufacturer;
2. First check the parallelism and straightness of the beam, and then check the parallelism and verticality of the finger;
3. If positioning with the bending edge, try to make this bend no greater than 90 degrees;