Key Factors Affecting Plate Rolling Machine Prices
Table of Contents
Machine Specifications Impact on Pricing
Tonnage and Maximum Plate Thickness
Roll Length and Diameter
Automation and Control Systems
Manual vs. Semi-Automatic vs. Full CNC Systems
Software Features and Licensing Fees
Build Quality and Material Selection
Frame Construction and Welding Standards
Surface Treatments and Corrosion Resistance
Accessories and Tooling Options
Back Gauge and Sheet Support Tables
Custom Roll Profiles
Manufacturer Reputation and Warranty
Standard vs. Extended Warranty Plans
After-Sales Support and Training
Frequently Asked Questions
Cost Impact of Automation Features
Are Higher-Capacity Machines Always Better?
Retrofitting Automation on Manual Machines
Conclusion
When evaluating plate rolling machine prices, understanding the core drivers of cost variation is essential. This analysis examines critical factors—from machine specifications to control system complexity—to facilitate informed purchasing decisions aligned with budgetary requirements.
Impact of Machine Specifications on Pricing
Physical dimensions are primary price determinants. Larger machines processing thicker/wider metal coils require reinforced frames and higher-power motors, directly increasing manufacturing costs.
Tonnage and Maximum Plate Thickness
High-tonnage models designed for thick-plate processing incur significantly higher costs. For example: Equipment handling 20 mm steel plates utilizes heavy-duty rolls and reinforced frames, substantially exceeding the cost of 8 mm capacity machines.
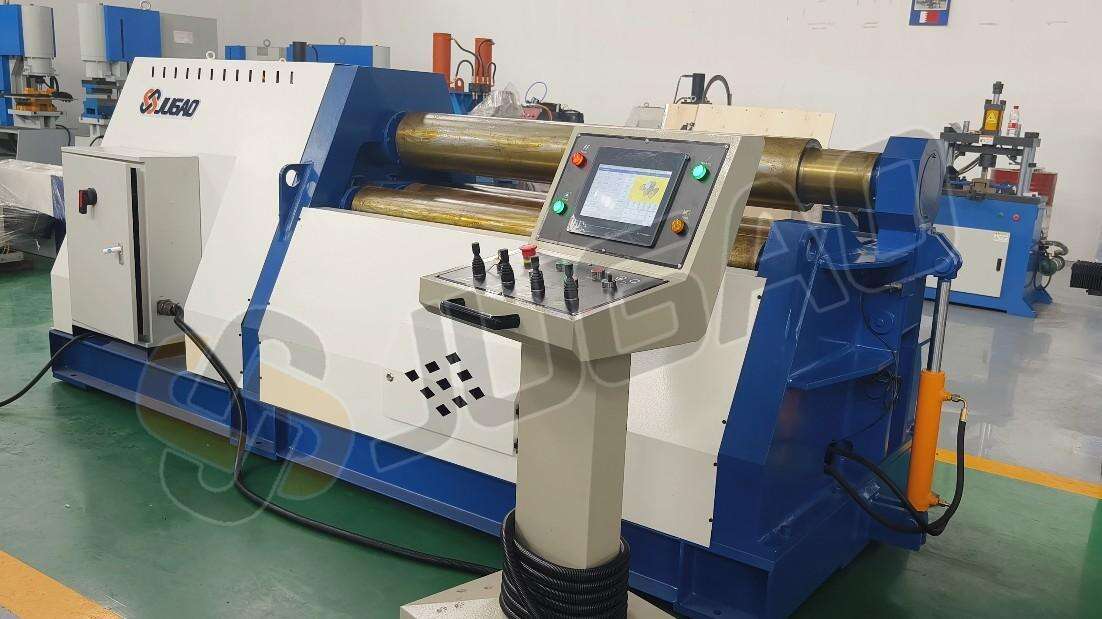

Roll Length and Diameter
Increased roll dimensions expand processing capabilities but necessitate precision bearings and structural reinforcements, elevating overall costs.
Automation and Control Systems
Automation levels critically influence pricing. Basic manual machines offer economy, while CNC systems command premiums for enhanced precision and repeatability.
Manual vs. Semi-Automatic vs. Full CNC Systems
Manual: Relies on handwheel operation and visual alignment—lowest cost but operator-dependent
Semi-Automatic: Incorporates hydraulic assists or basic back gauge positioning—moderate cost with improved consistency
Full CNC: Integrates programmable logic controllers (PLCs), touchscreen interfaces, and automated positioning—highest cost for maximum precision and minimal manual intervention
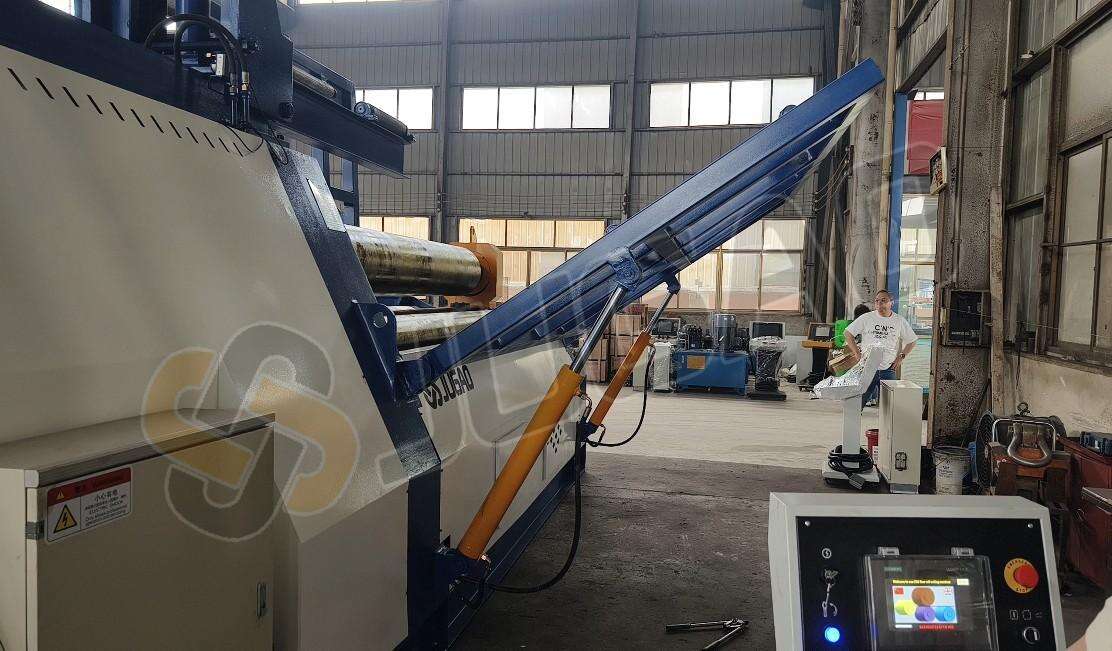

Software Features and Licensing Fees
Advanced software with nesting capabilities or custom bend sequencing typically incurs additional licensing fees, potentially increasing base machine cost by 5–10%.
Build Quality and Material Selection
Manufacturing standards directly affect machine durability and pricing.
Frame Construction and Welding Standards
Frames fabricated to industry standards (e.g., ISO 3834) with stress-relieved welding resist deformation but increase production costs.
Surface Treatments and Corrosion Resistance
Powder-coated frames and stainless steel rolls—essential for processing corrosive materials or operating in humid environments—significantly elevate procurement costs.
Accessories and Tooling Options
Customizable add-ons optimize workflow efficiency but increase total investment.
Back Gauge and Sheet Support Tables
Hydraulic/electric back gauges enhance repeatability, while motorized support tables facilitate large-coil handling—both improve productivity at added expense.
Custom Roll Profiles
Specialized roll contours for cylindrical shells or decorative forming may increase base machine prices by 15–20%.
Manufacturer Reputation and Warranty
Purchasing from established manufacturers like JUGAO involves premiums but provides three critical assurances: verified reliability, global service networks, and comprehensive warranties.
Standard vs. Extended Warranty Plans
Standard 1-year warranties are typically included; extended plans covering 3 years or full spare parts may increase prices by 8–12%.
After-Sales Support and Training
On-site installation, operator training, and preventive maintenance contracts require upfront investment but ensure long-term operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cost impact of automation features?
Upgrading from manual to semi-automatic increases base price by 20–30%; full CNC systems (with touchscreens and advanced software) raise costs by 40–60%.
Are higher-capacity machines always superior?
Not necessarily. Oversized equipment leads to underutilized capacity and unnecessary expenditure. Select models matching your typical plate thickness and width requirements.
Can automation be retrofitted on manual machines?
Some manufacturers offer retrofit kits for hydraulic assists or digital readouts. While cheaper than new machines, retrofitted solutions generally deliver lower precision and reliability than purpose-built CNC systems.

Conclusion
Understanding variables affecting plate rolling machine prices enables accurate quotation comparisons and optimal model selection. From processing capabilities and automation levels to build quality and manufacturer support, each factor influences the total investment value.